Bringing
it all together – a brand new explanation of the experimental observations of
frequency and power windowing in electromagnetic interaction with biology Hz- GHz, effects of modulations, wound
healing, cancer induction/promotion and subtle field cancer treatment’ By
Dr Chris Barnes, Manager
@bsec-wales.co.uk
A new hypothesis has been formulated
which brings together Bose Einstein ( Frolich ) condensate ‘Geesink’ modes and Ion Parametric Resonance. Key frequencies
work in concert with Schumann resonance to normalise biological systems at an
ideal DC field strength. The
hypothesis enjoys strong support in a number of directions. For example, the
prediction that cancer incidences would vary according to the earth’s
background DC field is fulfilled. A
number of healing frequencies are fully explained in terms of the particular
ion channel being disturbed especially pertinent to cancer wherein cancer cells
some ion channels are overexpressed. Perturbation of very specific ion channels
also explains dangerous effects of RF on biology. Activation of voltage gated chloride
channels is most dangerous and
explains the few observations
of RF at harmonics of 455-457 Hz as
being genotoxic and a mechanism by which
RF can generate ROS. Under normal
circumstances THE BODY CAN COPE WITH THIS but I propose that if voltage gated
channel TRPM7 is also modulated by
excessive frequency sources at harmonics of 320-374 Hz both additional oxidative and nitrosative
stresses occur and either
initiation of cancer could follow or highly likely promotion of existing cancer will follow. This could account for why certain cancer
latency or reoccurrence periods appear to be reducing. Certainly ionising radiation has this effect
for breast cancer, see Nguyen et al
(2011). Another great success of the
theory is to explain why the team of Zimmerman and Pasche were able to use
physiological heartbeat changes to define their so called ‘TTF’ tumour treating
frequencies. The same sorts of ion
channels expressed in heart muscle and nerve fibres are also expressed in many
cancer cells but not so much normal non-excitable tissue. The theory also explains Hallberg’s observations of FM radio and melanoma. Finally, regarding power windowing, the limit
of human sensitivity is of the order of 1picotesla, i.e. pretty much the same
as Schumann resonance.
Introduction
We
are of late truly a society, rather now an entire globe, bathed in
anthropogenic electromagnetic radiation.
Few question if that radiation will have upon us either deleterious or
positive effect. The standard ‘physics’
based answer is to suggest that unlike x-rays or nuclear radiation this radio
frequency stuff is tame. Its flux quanta
per se do not have enough energy to break chemical bonds or cause ionisation so
we can forget about it. Further because
results in the mainstream experiential academic literature appear so
conflicting with regards to the effects of RF radiation this has led to those
charged with administering its safety having to set almost arbitrary limits
which also vary considerably from country to country across the world.
In
this paper we will see that ‘Frequency’ is an operative word. Waves of any ‘frequency’ be they
compressional or longitudinal proceed carrying a pattern in time and space, if
they carry modulation or information, that train of information too proceeds adding
complexity to our ‘pattern’ in time and
space. Next week meet biological
reactions. These do not employ inanimate chunks of ‘test tube’
chemistry. They too proceed in the four
dimensions of time and space carrying information with them or transferring it
from place to place in a manner as to create order from chaos, negative entropy
and coherence. This biological coherence manifests at all
sorts of levels, from the thought that creates a paper or publications such as
this, to the firing of motor neurones causing muscular contraction and the very
muscular contraction itself as the keys of the key board are struck. But what of the subtler, sub -cellular and
even sub-molecular interactions. If the
components move in time and space, then frequency must play a part. In other words, biology and frequency far
from being un-interactive, as our traditional
high school physics book might suggest, are in fact inseparable.
Further
it becomes quite conceivably that ‘frequency instructions’ encoded in both the
primordial micro, sub atomic particles of the initial big bang encoded the
inanimate but more ‘macro’ such as water and especially certain clathrates providing
THz frequencies to ultimately allow initially by RNA replication and later with
the whole suite of bio-molecules we are familiar with, i.e. life as we know it. Moreover, the development of our ancestral
DNA began in a time when there was only natural frequency present. If we limit ourselves to the frequency range
Hz-GHz which is the subject matter of this present paper then these natural
frequencies would have included as regular inputs Schumann resonances of our
Earth and other planets and broad band microwaves from solar and galactic
inputs. However, there would have been
protective ‘notches’ in these microwave emissions, wherein their amplitudes
would have been reduced over very narrow band regions due to the various
atmospheric microwave absorption lines of gases and radicals. Thus at least, if nothing else, we owe it our
creation, however brought about, to enquire about the effects of anthropogenic
or extraneous frequency and notwithstanding the safety of our offspring.
The
average man, woman or child’s exposure, particularly to UHF and microwave frequency
electromagnetic radiation has increased very substantially over the last two
decades with the now very ubiquitous use of both the mobile phone, and wireless
devices in general. We are all too exposed to ELF (extremely low
frequency) radiation in the form of domestic electricity supply electric and
magnetic fields at 50 or 60 Hz and their multiple and sub-harmonic
frequencies. In this regard so too did
our parents and grandparents suffer some exposures, although it could be argued
that with the increase in electrical and electronic appliances in households in
general, even ELF exposure is on the rise.
Even in our cars and buses we are not immune from Bluetooth and WIFI
exposure or the ELF fields from the ECU and wiring loom.
Clearly,
there are those concerned about safety aspects of such exposure. Such concerns are in part prompted by
anecdotal reports of symptoms such as but not exhaustively; sleep disturbance,
headaches, skin tingling, ringing in the ears, anxiety, palpitations, immune
disturbances and the like in the vicinity of mobile phone masts and wifi
networks. In the past such symptoms have
been put down to EHS ( ecltro- hypersensitivity syndrome) or simply thought of as being
psychosomatic.
However,
when proper epidemiological studies are conducted which validate some of the
above one starts to address more serious concerns. For
example, we see a growing tide of unexplained mental illnesses in teenagers and
young adults and increases in certain types of cancer. It is certainly instructive and we can
perhaps learn from taking for comparison a small slice of society which does
not use or at least avoids as far as practically possible the use of modern
electromagnetic technology, namely the Amish religious sect. The
Amish (/ˈɑːmɪʃ/; Pennsylvania Dutch: Amisch, German:
Amische) are a group of traditionalist Christian church fellowships with Swiss
Anabaptist origins. They are closely related to, but distinct from, Mennonite
churches. The Amish are known for simple living, plain dress, and reluctance to
adopt many conveniences of modern technology. The history of the Amish church
began with a schism in Switzerland within a group of Swiss and Alsatian
Anabaptists in 1693 led by Jakob Ammann. Those who followed Ammann became known
as Amish. Many Amish emigrated to the
USA, Pennsylvania and Ohio where eve today they still follow their strict
religious traditions which somehow seem to confer upon them protection from
certain illnesses and diseases. I postulate that these are ‘frequency’
diseases.
Intriguingly,
teenage mental illness and related conditions such as ADHD and autism are
extremely rare amongst the Amish.
Cancers too are some 40% less in occurrence than in the rest of Ohio.
Cancer
these days inevitably seems to be everybody’s prime concern. There are so many cancer related articles
on the media and indeed with between 1 in 2 and 1 in 3 of us destined to suffer
from it especially in old age we can’t but help know someone somewhere touched
by it.
Occasionally
in the media and often in the scientific literature one comes across claims of
association of cancer with RF radiation.
Yet equally just as often one comes across published scientific papers showing no correlation whatsoever or
even beneficial effects of RF
Radiation. Based on these
results it has been incredibly difficult, if not impossible, for those
committees charged with setting safe limits on Radio Frequency Field strength
to protect our health. Over the years
this has manifest in different safe limits being set in the USA, Russia and
Europe with respect to RF radiation and even to its classification
as a possible carcinogen by the WHO.
Studies
of the effects of RF radiation on biological material began several decades ago
by treating biological material, blood, tissues, protein and the like as dielectric material. Thus some idea of polarizability,
displacement current, loss tangent and energy dumping or dielectric heating
could be obtained. There is of course
no question that high power RF radiation
sets up currents in tissue and damages it by thermal mechanisms. One only has to look at a radio frequency
burn, for example. Similar mechanism is exploited in microwave
cookers where the dielectric heating is due to phase lag between ‘wagging’
hydrogen bonds in free and food bound water.
However,
the field strengths that we are exposed to every day from our mobile phones.
Wifis, TV and Radio Broadcasting and domestic wiring are at least 1000 times
less than those of a high power radio transmitting antenna or microwave over and in some cases even over a million times
less. These are the types of field
strengths which do not cause heating of tissue but have by about 50% of studies
being reported to cause often subtle biological effect.
A
substantial number of studies on electromagnetic radiation reach the conclusion
that unmodulated radio waves are safe.
The trouble is in the modulation, particularly if it carries ELF
pulses. Prima fascia I have a certain
degree of sympathy with this, although it is by no means the entire story. Taking the radio science point of view, an
unmodulated carrier carries with it no information, only the modulation carries
information. But I will show this is not
strictly true. It can only be true if
either the carrier wave is infinitely off, i.e. has never been on, or is
infinitely on. So in a biological
experiment the carrier would need to have been on at a time preceding the birth
of the organism being tested. Otherwise
as it switches on, it advertises its presence.
In the simplest sense modulation can be an on-off carrier wave, for
example, Morse Code. There is another
way an unmodulated wave could appear to show information. In this case if it is reflected or partially
reflected in a cavity, such as in a room in house or a vehicle as to form a standing
or stationary wave. Passing through
peaks or troughs in the standing wave which occur at twice the frequency of the
original wave one will ‘feel’ information.
Indeed, there is a scientific study in the literature (albeit a solitary
study) which shows just this.
Following
from Geesink’s hypothesis of the bio-soliton clathrate resonator and Frolich
style frequency condensates there ought to be a whole family of unmodulated RF
carrier waves which show biological effects, with frequencies form Hz to THz.
I
have been able to find a handful of such frequencies in the recent studies, of
others which the less well informed might be tempted to dismiss because of the
apparently overwhelming loading in favour of the need for modulation to provoke
biological effect. However, I am not
the only one to provide the solution.
Reference to ……. Is very instructive.
They give specific GHz frequencies which provoke biological effect
without modulation, their so called ‘effective’ frequencies and those which
require ELF modulation in order to bring about effect. The latter being
referred to as their so called ineffective frequencies.
The
question of science apparently having disclosed so few ‘effective’ modulation
free frequencies can be addressed quite simply by delving into
the needs of the majority of modern studies on RF-biology interaction which
have been motivated purely by the need to assess the safety or otherwise of
mobile technologies, consequently only a handful of RF carrier frequencies have
been addressed. These are typically and mainly frequencies
associated with modern mobile telephony and WIFI, 835 MHz, 900 MHz, 915 MHz,
935 MHz, 1.8 GHz, 2.1 GHz, 2.45 GHz. It
is this of course perfectly understandable they have been studied. Very occasionally studies refer to other
frequencies for example: 50 MHz (analogous to old Band 2 TV or a VHF amateur radio band, 147 MHz, another VHF ham
radio band and close to the band used for high power radio pagers, much higher
microwave frequencies in the region of 40-60 GHz used in point to point
microwave mobile telephony back haul and in some Russian subtle field treatment
units.
What
is perhaps somewhat more surprising and frightening is that we are all bathed
in, and have been for a several decades, lots of other radio and TV
broadcasting frequencies, form the KHz to the high hundreds of MHz which have
simply not been explored under laboratory conditions at all. The only studies here seem to have been of
geo-spatial epidemiological types with rather inconclusive outcomes. This is hardly surprising in the light of
the fact that most TV broadcasting stations emit multiple frequencies TV, FM,
DAB all from the same antenna mast or
location.
Returning
to the literature then, effectively then about a dozen or so frequencies, or
frequency channels (if modulation has been included) have been discussed in the
literature their bio-effect. Even if we
limit ourselves to frequencies up to 1 GHz and a 10 KHz channel this the leaves
the interaction of 100,000 channels and
biology totally unexplored. About a sixth of the known frequencies studied
to date have modulation independent biological effects even though this
represents only some 3 of about 5000 studies in the literature. This is because
so much duplication has been attempted using modulated frequencies, which when
we face reality is what we are more usually exposed to. However, the numbers remain
interesting. It suggests that within the
frequency space to 1 GHz even allowing for channelization there should be about
16,000 more very biologically active frequencies. This is not so unlike the estimated
19,000-20,000 human protein-coding genes.
My proposal is that frequency medicine, once condemned to the realms of
quackery, will one day soon be very much on the cards.
Hypothesis: Bringing it all together:
Combining the best.
Part (i) Frequency windowing.
No
one present theory presently or adequately explains the interaction of
frequency with living biological material at a whole organism level or at a
cellular level or at a sub-cellular level.
Given the above this is perhaps hardly surprising. Some models
however come remarkably close. The
standard ion cyclotron resonance model (ICR) describes ELF frequencies at which
common biological ions may be driven in spiral paths through active transport
membrane channels in the presence of the of the earth’s magnetic field. Most references quote the ICR frequency for
the calcium ion as 16 Hz. Changing rate
of ion influx from extra- cellular position to the interior or vice versa (efflux)
has biological effect because of the knock on effect on up or downstream
processes. Probably this is why 16 Hz
amplitude modulation has featured heavily in several biological studies of RF
radiation.
ICR
however has its limitations and does not account for all observations. Lednev
(1991) was perhaps the first to have significantly added to the ICR model by
producing perhaps the first model which could loosely be described as Ion
Parametric Resonance (IPR). IPR defers
from ICR in that it takes into account the AC magnetic field strength that the driving
frequency is applied at in addition to DC field strength which in a normal
biological system would be a vector component of the earth’s field. IPR
also predicts biological effects at additional frequencies which are the
sub-harmonics and harmonics of the ICR cyclotron frequency. Thus I also believe Jacobson resonance, a general form of Zeeman
and cyclotron resonance, to be an extension predictable by IPR.
According
to Lednev, an ion inside a Ca2+ -binding protein is approximated by a charged
oscillator. A shift in the probability of ion transition between different
vibrational energy levels occurs when a combination of static and alternating
magnetic fields is applied. This in turn affects the interaction of the ion
with the surrounding ligands. The effect reaches its maximum when the frequency
of the alternating field is equal to the cyclotron frequency of this ion or to
some of its harmonics or sub-harmonics. Most importantly a resonant response of the
biosystem to the magnetic field results. Once we have resonant responses we can begin
to understand more easily how very subtle fields might influence biology.
Very
importantly, the IPR model has been testable experimentally, see Blackman et al
1999.
They
used hydrogen ion IPR and PC-12 nerve cells to make the test. Because the
charge-to-mass ratio of hydrogen is much larger than any other biologically
significant ion, hydrogen resonance provides a unique test case by which a
single ionic bandwidth can be clearly measured. Their work
considered the response of
nerve-growth-factor-stimulated PC-12 cells exposed to magnetic fields tuned at
or near hydrogen resonance. Further
their work was designed to test the IPR model prediction of an approximate -/+10% ionic bandwidth. Consistent with the
work of Trillo et al., resonance conditions were established using a 2.97
microT static magnetic field, and the AC frequency and field strength varied to
prove different aspects of the resonance. With this static field, 45 Hz was the resonance frequency identified
for hydrogen, 42.5 and 47.5 Hz were near-resonance frequencies, and 40 and 50
Hz bounded the assumed -/+10% hydrogen resonance bandwidth. The cell responses at 45 Hz exposures agreed
with the IPR model predictions and replicated results obtained by Trillo et al.
Cells exposed to 42.5 and 47.5 Hz (near resonance) magnetic fields responded in
the same general pattern as those exposed to 45 Hz fields, but neurite
outgrowth was less than that observed at resonance. Measured results for cells
exposed to either 40 Hz or 50 Hz fields were indistinguishable from
off-resonance responses, consistent with the hypothesized bandwidth. These
results confirm that the response bandwidth for the hydrogen ion is no greater
than -/+10%, and give further support to the resonance-based predictions of the
IPR model.
Despite
this experimental proof of IPR there has
remained criticism of the model because of factors such ion residency time and
signal to noise ratio. Machlup (2009)
provides the solution as follows. Lednev's
“possible mechanisms for the influence
of weak magnetic fields on biological system” involved two parallel magnetic
fields, one constant and one oscillatory in the ELF (extremely low-frequency)
range. The suggested ion resonances (IPR) were termed “impossible” by Adair (ref
) even after the above referred demonstration in a rat-nerve (PC-12) cell
culture. Machlup (2009) resolves the
“signal-to-noise-ratio” paradox by taking account of the coherent absorption of
the ELF energy and showing how the energy of several trillion ELF photons can
free a single ion from its trap on the surface of a cell of the culture.
All
we require is evidence of such coherent absorption and it is that I believe I
can show. The simple fact is everything
needed for this deduction is already out there in the literature. It is simply that no one author or
experimenter has had either the time or inclination to bring it all
together. This work is very much
quantum biology and here I am reminded of one the sayings of my late mentors who
was involved in this field and whom I first met at the ripe old age of 89 some
four years before his death, namely that of Albert Szent-Györgyi von Nagyrápolt who is
quoted as coining the phrase ‘Discovery
is seeing what everybody else has seen, and thinking what nobody else has thought’.
At
about the same time that Szent Gyorgyi was contemplating the redox chain and
free radicals in cancer, Herbert Fröhlich whom I also met at a conference in
Nottingham University was providing his biological quantum coherence
theory. Moreover, the theory proposes the so called
Frolich condensate, a sort of Biological equivalent of the Bose-Einstein
condensate.
Evidence
of the Frolich condensate ought to be found in large biological effects arising
from minute temperature changes.
Obvious examples are the exquisite sensitivity of the human eye and ear
even at close to thermal energy. Webb et
al (1977) provided evidence from the bacterial world. The ratio R of the intensities of anti
Stokes and Stokes Raman shift lines of 124 cm-1 and of 118 cm-1 of active E.
coli B was measured. For an oscillating system in therm equilibrium R ≈
0.55 is expected whereas they found R ≈ 1.0. This shows that this system was
excited strongly above thermal excitation in agreement with a Frolich style theoretical conjecture.
In
1985, Frolich himself, provided further experimental evidence for his
theoretical model. Large biological
effects arising from very small temperature differences — when overall changes
of temperature have negligible effect — support the theory of coherent
excitations. Establishment of a spectroscopic resonance in the membrane of
erythrocytes confirmed his theoretical estimate.
Grundler
(1977) provided yet further evidence, this time for coherent energy conversion,
in that the growth behaviour of yeast cultures in aqueous suspension was
monitored by visible light extinction and showed an exponential growth rate
reproducible within ±3% limits. When the
cultures were irradiated by c.w. microwave fields of a few mW/cm2 the growth
rate either stayed constant or was considerably enhanced or reduced depending
on the frequency around 42 GHz. A spectral fine structure with a width of
the order of 10 MHz was observed. Careful temperature monitoring had excluded a
trivial thermal origin of this effect.
Lundholm
et al (2015) are perhaps the first to show Frolich condensation in non-lving
biological material. They have shown
that Terahertz radiation induces non-thermal structural changes associated with
Fröhlich condensation in a protein crystal.
It was proposed by Fröhlich that vibrational modes within protein
molecules can order and condense into a lowest-frequency vibrational mode in a
process similar to Bose-Einstein condensation, and thus that macroscopic
coherence could potentially be observed in biological systems. Despite the
prediction of these so-called Fröhlich condensates almost five decades ago,
experimental evidence thereof has been sparse, indeed Lunholm at the time of
writing didn’t even appear to be aware of the references I have presently
generated. Effectively they have found
the first experimental observation of Fröhlich condensation in a protein
structure. To that end, and to overcome the challenges associated with probing
low-frequency molecular vibrations in proteins (which has hampered
understanding of their role in proteins' function), they combined terahertz
techniques with a highly sensitive X-ray crystallographic method to visualize
low-frequency vibrational modes in the protein structure of hen-egg white
lysozyme. They found that 0.4 THz electromagnetic radiation
induces non-thermal changes in electron density. In particular, we observed a
local increase of electron density in a long α-helix motif consistent with
a subtle longitudinal compression of the helix. These observed electron density
changes occur at a low absorption rate indicating that thermalization of
terahertz photons happens on a micro- to milli-second time scale, which is much
slower than the expected nanosecond time scale due to damping of delocalized low
frequency vibrations. Their analysis shows that the micro- to milli-second
lifetime of the vibration can only
be explained by Fröhlich condensation.
Srobar
(2014) extends Frolich’s original model. Oscillating polar entities inside
biological cells, most notably microtubules, were discussed in terms of their
tendency to emit electromagnetic radiation. This phenomenon is described by
Fröhlich kinetic equations expressing, in terms of quantum occupancy numbers of
each discrete collective oscillatory mode, the balance between incoming
metabolic energy flow and losses due to linear and non-linear interactions with
the thermal environs of the oscillators. Hitherto, radiation losses had not
been introduced as part of the balance; it was assumed that they were proportional
to the modal occupation numbers. Srobar demonstrated that this formulation is
incorrect and the radiation losses must be taken into account in the kinetic
equations explicitly. Results of their numerical study of kinetic equations, enlarged
in this sense, are presented for the case of three coupled oscillators which were
shown to evince the essential attributes of the Fröhlich systems. Oscillator
eigenfrequencies were chosen, alternatively, to fall into the MHz and the THz
frequency domains. It was found that large radiation levels destroy the main
hallmark of the Fröhlich systems, the energy condensation in the lowest
frequency mode. The system then functions as a convertor of metabolic energy
into radiation. At more moderate radiation levels, both energy condensation and
significant radiation can coexist. These results also suggest that quantum
coherence in biological systems and coherence between the modes of such systems
and external pump frequency waves will be more likely at extremely low power
levels. Typical estimates of power
outputs of single living cells are between 10^-20 W and 10^-1o W so certainly
not inconsistent.
Geesink
and Miejner (2016) have very recently indeed provided a bio-soliton model for
the very origins of primordial life at hydrated clathrate surfaces, their so
called quantum RNA replicator.
Furthermore when the THz frequencies of the replicator are reproduced on
an acoustic condensate scale of some
240 -500 Hz by successive division by two they claim that the frequencies of a
large number of RF effects style biological experiments
similarly reduced either line up with their condensate frequencies ( their so
called life -sustaining frequencies) or lie in bands in-between, these being
their so called life destroying frequencies). Close examination of their results shows the
number of references to life -sustaining results strongly outweighs references
to life destroying results and most of the references are not readily found in
internet searches. This is a great
shame as I do believe there is ultimately significant substance in the general findings
of Geesink and Meijer. I will show that
when more references are considered biological effect can sometimes be either
positive or negative at or in-between the Geesink/Frolich style
condensates. I will show that the only
explanation for this is that biology has used specific condensates for specific
processes some in conjunction with IPR to bring about augmentation or depletion
of specific biological ion channels not just calcium as has previously been
suggested. Indeed, I will show that in my model, hereinafter the Barnes
model, an adaption of the Geesink resonator idea marries exactly
with IPR and with Jacobson Resonance and leads me to the point where not only
can I explain frequency windowing, I can also predict which specific voltage
gated ion channels are being disturbed by each frequency window and what
precise biological effects are to be expected.
In other words, I
believe for the first time ever I can open up true frequency medicine for wound
healing, brain disorders, cancer treatment and the like and that it will be able to be used precisely
and not with hap-hazard as has been the
case in the past. Similarly, I will be
able to predict biologically safe frequencies and modes for radio, TV and data
transmission.
Developing the Barnes model
My
present model proposes the following.
Firstly, that Geesink/Frolich condensate modes provide energy for active
transport and other processes by parametric conversion from broad band
microwave background. Favoured modes
are those which coincide with IPR and especially coherently with Schumann
resonance, from where additionally millions of ELF photons can be trapped over
coherence time to provide sufficient membrane vibration energy to move ions off
cellular surfaces and they are propelled in voltage gated channels by ICR spiral
like forces. IPR and Geesink/Frolich condensate can be stimulated at even
harmonic and
sub-harmonic frequencies and thus this explains why biological processes are
perturbed by such a vast range of frequency.
The
following are used in developing and testing the model:
1.
First
I take the Geesink condensate frequencies and add Schumann resonance bands and
atmospheric microwave attenuation notches.
The logic here is that primordial life would have developed utilising
the whole electromagnetic background available not just the output of the
clathrate RNA resonator. The broad band
input component providing general energy for conversion to coherent modes. The Schumann inputs working in conjunction
with specific IPR resonances and specific voltage gated ion channels to drive
specific biological processes.
2.
Secondly,
I add in as many results of the biological outcomes from extraneous RF – biology
interactions such as those of human, animal, xenograft and cell culture studies to inform and test
the model. Proof will be seen in
particular types of effects being seen as specific to specific condensates and
the same being excited by their frequency multiples and sub –multiples across a
large range say Hz-GHz.
3.
Thirdly,
because IPR depends on local DC magnetic field model predicts that cancer rates
should increase in regions of the world where DC field is very different from
average, irrespective of other variables.
This should happen as IPR’s which coincide with a particular Schumann
resonance mode or beneficial condensate are moved frequency wise relative to it
because of changes in local (DC) magnetic field and this also gives a new an
alternative explanation to certain types of cancer clusters.
4.
IPR
model suggests bandwidth of up to 10% .
Bio-soliton model only allows bandwidth of 1.5%. Should result in specific ions being
associated with groups of *biological processes or small bands across
condensate and gaps in-between condensate, so called anti-condensate according
to Barnes. When AC magnetic field is
factored in predicts power dependent
effects or power windowing because power ‘tunes’ IPR frequency ( probability and direction of ion
in channel) across narrow band of condensates and will explain sometimes
observations of positive and negative bio-effects for more or less same or
similar experiment, hence ‘defuses’ controversy attached to topic in
literature. *
Again elegant evidence of this is provided from considering hitherto
misunderstood results of others.
Step
by step construction by way of frequency tables is now shown.
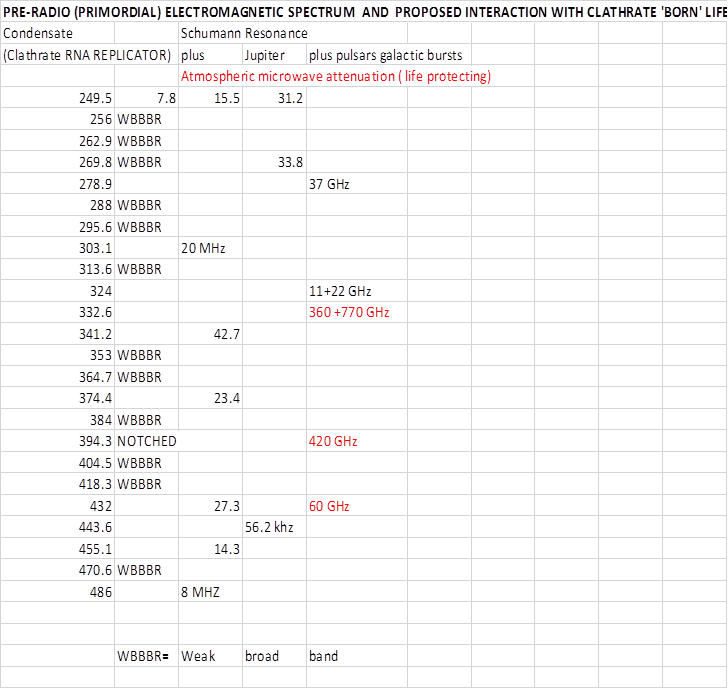
Table 1 : Geesink’s clathrate replicator
‘condensate’ frequencies showing planetary inputs and broad band microwave in
black and
Notched frequencies protected by
atmospheric absorption in red.
Thus
this first stage in the Barnes model predicts that we should find some life
critical biological processes associated with either the Schumann resonance
reinforced condensates or the notched
‘protected’ frequency condensates. Furthermore perhaps the most critical of all
processes ion transport as to allow muscular contraction as in a mammalian
beating heart ought intuitively to be on the lowest frequency condensate. In table 2,
I inspect what is found in the literature regarding the results
of radio frequency and ultrasound frequency experiments on biological systems
and insert effects on these ‘key’ frequencies above.
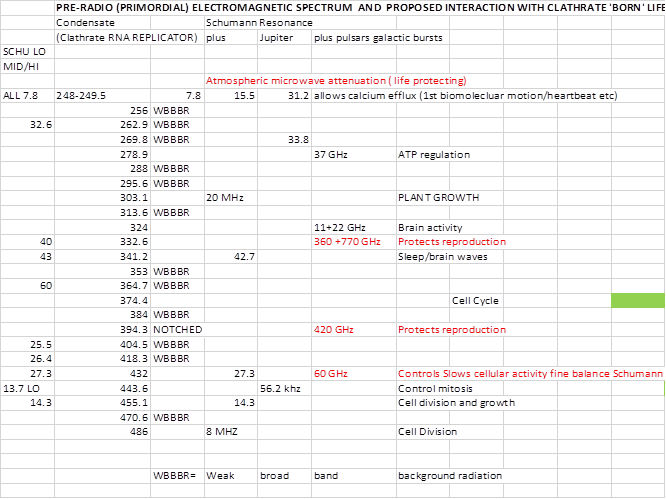
Table 2: Frequencies as per Table 1 with deduced
biological processes inserted.
Immediately
it can be seen that the hypothesis is strongly supported. The first Schumann resonance is an exact
sub-multiple of the lowest frequency condensate at 256 Hz and all known
experiments across a wide range of frequency associate this mode with modulation
of calcium channels. Calcium (Ca) is
the key regulator of cardiac contraction during excitation–contraction (E–C)
coupling fundamentally the most important process to all higher life forms. ATP regulation would seem to be associated
with narrow band galactic microwave input at 37 GHz. Plant growth is both positively and
negatively affected by frequencies which are harmonics of the condensate on
303.1 Hz. The 20 MHz input in primordial
times as today is due to Jovian signals, amongst some of the strongest natural short wave radio sources here on
earth. Experiments with RF which has
even sub-harmonics coinciding with the family of condensates from 324 to 341.2 Hz
show teratogenic effects and influence
brain activity. I tentatively therefore
suggest that the atmospheric attenuation at 360 and 770 GHz was crucial in shaping the process of meiosis
in balance with input from the
approximately 40 Hz Schumann resonance.
In mammals the primitive brain differentiates very early in gestation
and this may account for the unlikely association. Calcium-dependent modulator protein in
spermatozoa are also similar to brain modulator protein, see Jones et al
1978.
Similar
teratogenic effects are found at a condensate frequency of 394.3 Hz which although a Barnes’
‘anti-condensate frequency’ also appears to be protected by atmospheric notched
attenuation.
Finally
there is a whole block of condensate frequencies which appear to be heavily
related to cellular division ( mitosis) and growth between 432 and 486 Hz. They were clearly heavily influenced by 2nd
and 4th Schumann resonance and KHz Jovian inputs.
It
is further instructive to insert known ICR frequencies of both hydrated and
non-hydrated small ions into the table.
It is adequate to use ICR frequencies because at zero or very low AC
fields strengths the ICR and the IPR frequencies are one and the same. However, one must choose a ‘standard’ value
of DC magnetic field and so I have
normalised ICR frequencies to the average earth magnetic field of 45 micro
Tesla. Hydrated and non- hydrated ion values are
shown because in some cases ions are ‘squeezed’ into exceptionally hydrophobic
regions. In making the calculation for
hydrated ions I have used the lowest number of water molecules of hydration for
each ion according to the available literature. I have also included as much information as
I can have gleaned from as many references as possible on the effects of RF
radiation from ELF to GHZ on even harmonics of
the Geesink condensates and the Barnes anti-condensates.
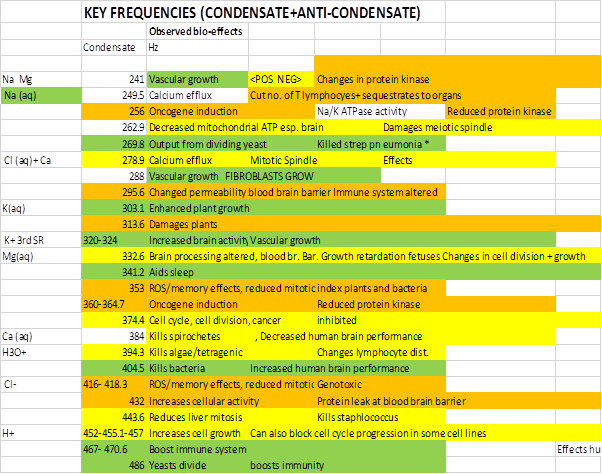
Table 3: Same data as Table 2 with common ion ICR
frequencies included.
Colour Key:
Green = positive biological effect; Orange = detrimental bio-effect.
Yellow= Bio-effect which could be adapted for treatment, cancer and the
like.
Perhaps
the most obvious observation form Table 3 is that rather than bio-effect being
alternating good and bad as suggested by Geesink and Meijer, when considerably
more results are analysed a patterns builds up of apparently pseudo random
blocks of good and bad, as per my contention and explanation above. This is because the quantum replicator and
Schumann resonance only varies by about +/-1.5% but IPR frequencies vary
according to the Earth’s DC field which varies from location to location and
there was obviously no control over this and no understanding of or desire to
do so when all prior RF -biology
experiments were performed, other than those specifically attempting to
validate ICR type hypotheses.
The
ultimate way to validate my present hypothesis is to examine closely the
literature associated with various voltage gated ion channels and biological
processes, particularly to see if the correct ion lines up with the observed
processes at each coherent condensate frequency of concern.
The 241 Hz condensate/ Na/Mg
TRPM7
is a divalent cation channel permeable to calcium and magnesium. It has been implicated as a signalling kinase
involved in vascular smooth muscle cell growth, apoptosis, adhesion,
contraction, cytoskeletal organization, and migration, important processes
involved in vascular remodelling associated with hypertension and other
vascular diseases. It seems a good candidate for the channel being perturbed by
RF radiation at harmonics of the 241 Hz
condensate working
synergistically with Magnesium IPR and is the first success for the Barnes
model.
The 249.5 Hz condensate/ Na (aq)
According
to Roselli and Jirillio (2006), several Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels (VGSC)
are widely expressed on lymphocytes and macrophages but their role in immune
function is still debated. Nevertheless, Na(+) influx through VGSC is required
for lymphocytes activation and proliferation, since these responses are blocked
by Na(+)-free medium or by VGSC blockers. These effects may be mediated by the
reduced intracellular Na(+) levels, which in turn may impair the activity of
Na(+)/Ca(++) exchanger resulting in reduced intracellular Ca(++) levels during
lymphocyte activation. Furthermore, in Jurkat cell line VGSC appear to be
involved in cell volume regulation, migration in artificial matrix and cell
death by apoptosis. VGSC play a role in macrophage function as well, and VGSC
blockers impair both phagocytosis and inflammatory responses. Several VGSC
blockers have shown immunomodulatory properties in mice models, skewing the
immune response toward a Th2-mediated response, while suppressing Th1-mediated
responses, and VGSC already used in clinical practice are known to modulate
immunoglobulin (Ig) levels both in mice and in humans. It looks consistent therefore that the 249.5
Hz condensate is operating synergistically with one of these voltage gated
sodium channels, a second success for the Barnes model. This is only half the story, however, for
this condensate both positive and negative bio effects are observed.
This is because Calcium ions in the external medium stabilize the
resting state of voltage-dependent channels, including Na channels. This effect
of calcium on channel gating is usually explained in terms of the surface
charge hypothesis, which proposes that local adsorption of calcium ion to the
outside of the membrane alters the intramembranous electric field, thus
influencing channel behaviour indirectly. Calcium ion has also been shown to
block Na channels, most strongly at negative voltage. Calcium most likely has a
gating effect and a blocking effect and
may be an essential cofactor in normal
gating and that it produces gating and blocking effects by binding within the
channel. We can now understand the bio-effect of ‘calcium efflux’ on a sodium
IPR frequency, a second complete success for the Barnes model.
The 278.9 Hz condensate/Ca2+ and Cl- (aq)
The
next frequency to be dealt with is 278.9 Hz where calcium efflux and mitotic
spindle effects are observed with RF radiation at appropriate harmonic
frequencies. According to my
calculations there are two potential synergistic ions which
are hydrated chloride and anhydrous calcium. The
notion and relevance of an ‘anhydrous’ ion may seem strange to some, but has
recently been discussed in the context of Nano pore channels, see
Aryal et al (2015), ‘Hydrophobic
Gating in Ion Channels’. I shall now
explore mitotic spindle effects. It has
recently been disclosed that calcium aids chromosome condensation prior to cell
division. Calcium-dependent regulator protein
is a low molecular weight (17,000), thermostable, calcium binding protein which
is structurally homologous to skeletal muscle troponin C., Thus the link between calcium concentration as
result of VGCC is established and as cells enter prophase, the distinct
cytoplasmic localization disappears commensurate with the dissolution of the
cytoskeleton. The regulator protein seems to be randomly distributed throughout
the prophase cell, including the region around the condensed chromosomes.
However, at prometaphase, it is localized in association with the half-spindles
of the mitotic apparatus. Through metaphase and most of anaphase, the protein
remains localized between the chromosomes and the poles of the spindle. During
late anaphase the protein is also found in the interzone region but rapidly
condenses into two small regions, one on each side of the midbody that
separates the daughter cells. The regulator protein is not localized in the
cleavage furrow during telophase, whereas actin is demonstrable in this region.
Indeed, placement of the protein during mitosis is distinct from both that of
actin and that of tubulin. The localization of calcium-dependent regulator
protein during mitosis suggests that it may mediate the calcium effects on the
mitotic apparatus and thus play a role in chromosome movement. Izant (1983) showed that An increase in the concentration of free
calcium ions during metaphase appears to stimulate the onset of anaphase. Keith et al (1985) using fluorescent
techniques confirmed this. This ability
to change the cell cycle may prove important in both RF cancer promotion and RF
inspired methods of treatment. Thus I
have shown the relevance of the synergistic relationship of anhydrous Calcium IPR and the 278.9 Hz condensate, I shall next deal with hydrated
chloride which has a more or less equivalent IPR frequency.
For
example, voltage gated chloride channels have been implicated in stem cell
mitosis in both normal and malignant glial cells and in particular in cytoplasmic
condensation, so called premitotic condensation (PMC). PMC represents an
obligatory step in cell replication and is linked to chromatin condensation. If
perturbed, the time required to complete a division is significantly
prolonged. PMC is a feature shared more
commonly among normal and malignant cells and that the reduction of cell volume
is accomplished by Cl− efflux through ClC3 Cl− channels. Habela et al (2008) used patch-clamp
electrophysiology and demonstrated a significant upregulation of chloride
currents at M phase of the cell cycle. Colocalization studies and
coimmunoprecipitation experiments showed the channel on the plasma membrane and
at the mitotic spindle.
For I believe therefore the Barnes’ model
elegantly accounts for the reported effects of RF radiation at the 278.9 Hz condensate working synergistically
with both types of ion present.
The 303.1 Hz condensate / K+ (aq)
AKT1
Potassium Channel is the major channel
controlling Plant Nutrition, hence
growth, see Hirsch et al 1998. The Barnes’ model marries Potassium IPR
exactly with RF effects at harmonics of the 303.1 Hz. Although shown as a positive effect, in
reality both positive and negative effects of RF have been noticed on plant
growth have been noticed especially
with UHF and microwave radiation. It is
hypothesised here that precise field
patterns and power levels will determine
if the IPR probability perturbation drives potassium influx or efflux. Essentially,
once again the model is a complete success.
The 322 Hz condensate/K+
Dealing
with the condensate centred around 322 Hz,
a diversity of voltage gated potassium
channels exist in brain with a diversity of functions. It seems quite feasible therefore that an
appropriate channel adequately stimulated by coherence of the condensate and IPR
frequency can bring about increased brain activity, again supporting the
Barnes’ model. Destruction or
mutation of KCNC3 causes the opposite effect e.g. neuro- degeneration. Autoimmune disease of these channels can
cause limbic encephalitis or CJD like symptoms. Regarding the observation of RF causing
increased vascular growth at this condensate,
recent work shows that several identified K+ channels are important in
both physiological and pathological cell proliferation, see Pardo 2004. Again everything here is fully consistent
with the Barnes model. Diabetes is
known to disrupt vasculature. Fully
consistent with the Barnes model it is perhaps not surprising that High Glucose Impairs Voltage-Gated K+
Channel Current in Small Coronary Arteries, see
Liu et al (2001).
The 384 Hz condensate/Mg2+(aq)
RF
radiation in general has been reported to cause both negative and positive
effects on neural function. Before the
present Barnes model, it would have been
virtually impossible to explain
why. Above we have seen how RF could
cause positive effects on cognition.
On the other hand at harmonics of
the 384 Hz condensate and in the presence of Hydrated Calcium ions and at
coherence with hydrated calcium IPR, it
would appear to cause exactly opposite and deleterious effects on human
performance and cognition. This can be
understood by looking at calcium metabolism in brain disease. For example, perturbed neuronal Ca2+
homeostasis is implicated in age-related cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's
disease (AD), see Bezprozvanny and Mattson (2008). With
advancing age, neurons encounter increased oxidative stress and impaired energy
metabolism, which compromise the function of proteins that control membrane
excitability and subcellular Ca2+ dynamics. Toxic forms of amyloid
β-peptide (Aβ) can induce Ca2+ influx into neurons by inducing
membrane-associated oxidative stress or by forming an oligomeric pore in the
membrane, thereby rendering neurons vulnerable to excitotoxicity and apoptosis.
AD-causing mutations in the β-amyloid precursor protein and presenilins
can compromise these normal proteins in the plasma membrane and endoplasmic
reticulum, respectively. Thus RF
perturbing and inducing Ca2+ influx
could produce an Alzheimer like state and accounts for reported memory
loss and perhaps dizziness and anxiety after certain RF exposures. Similalry in rats with brain injury, neuroprotection is afforded by SNX-185, an N-type voltage-gated calcium
channel blocker, see Lee et al
(2004). Once again everything discussed
here is 100% consistent with my model.
394.3 Hz condensate/Hydronium
I
next turn to the harmonic of the hydronium ion IPR in coherence with the
condensate at 394.3 Hz. Effects of RF at
higher harmonics of this condensate frequency are reported to alter Lymphocyte
distributions. According to DeCoursey
(2010) the voltage-gated proton channel bears surprising resemblance to the
voltage-sensing domain (S1–S4) of other voltage-gated ion channels but is a
dimer with two conduction pathways. The proton channel seems designed for
efficient proton extrusion from cells. In phagocytes, it facilitates the
production of reactive oxygen species by NADPH oxidase. Savina et al (2006) teaches that to initiate
adaptative cytotoxic immune responses, proteolytic peptides derived from
phagocytosed antigens are presented by dendritic cells (DCs) to CD8+ T
lymphocytes through a process called antigen “crosspresentation.” The partial
degradation of antigens mediated by lysosomal proteases in an acidic
environment must be tightly controlled to prevent destruction of potential
peptides for T cell recognition. They also describe a specialization of the
phagocytic pathway of DCs that allows a fine control of antigen processing. The
NADPH oxidase NOX2 is recruited to the DC's early phagosomes and mediates the
sustained production of low levels of reactive oxygen species, causing active
and maintained alkalinization of the phagosomal lumen. DCs lacking NOX2 show
enhanced phagosomal acidification and increased antigen degradation, resulting
in impaired crosspresentation. Therefore, NOX2 plays a critical role in
conferring DCs the ability to function as specialized phagocytes adapted to
process antigens rather than kill pathogens. Current theories on infections
with intracellular bacteria, protozoa, and fungi support the notion that MHC
class II-restricted CD4+ T cells are activated and that resistance depends
exclusively on this T-cell subset. Here, Stefan Kaufmann summarizes recent
evidence that in these infections MHC class I-restricted CD8+ T cells are also
activated, and participate in protection; they appear to lyse infected target
cells and produce gamma-interferon in vitro. Thus we have link, albeit rather complex
between RF exposure, the hydronium ion
and the observed changes in immune cell distribution. Once again,
the present Barnes model is fully vindicated.
It
is further extremely interesting to note that here we also have a quantum biological mechanism for RF to
generate ROS in biological tissue at minute power levels without needing to resort to complex intermediary mechanisms
such as altered water structure at liquid/gas interfaces (refs).
RF
applied as harmonics of the 394.3 Hz condensate in association with
hydronium IPR also is reported to cause teratogenic
effects in some bio-systems.
Gawad
Gad (MSc Thesis 2015) discusses a recombinant protein in the Xenopus oocyte
heterologous expression system, hCNT3 has been shown to have a Na+:uridine
coupling ratio of 2:1, in contrast to hCNT1/2 which have Na+:uridine coupling
ratios of 1:1. One of the two Na+-binding sites of hCNT3 also accepts H+. Recently,
the crystal structure of a bacterial hCNT ortholog (vcCNT from Vibrio cholerae)
has been reported. Based upon the crystal structure of vcCNT and previous
mutagenesis studies of hCNTs, four amino acid residues (N336, V339, T370, and
I371) were postulated to coordinate Na+ (and hydronium ion) binding within the
primary cation-binding site of hCNT3. To test this hypothesis,
electrophysiological studies were performed on oocytes producing wild-type
hCNT3 or engineered forms of the transporter in which each of the four residues
were individually mutated to cysteine. The results show marked changes in Na+-
and H+-coupling consistent with these residues forming the primary
cation-binding site of hCNT3. Mutation of the corresponding residues in hCNT1
and characterization of wild-type and mutant forms of vcCNT in oocytes provide
supporting evidence for her conclusion.
The argument I would advance is that if H+ levels are critical for hCNT3
then RF can disturb it and hence
damage oocytes and hence cause teratogenic
effects. Once again this is entirely
consistent with the Barnes model involving only quantum coherence and IPR
harmonics.
417 Hz condensate/ Cl-
I
now turn to the anhydrous chloride IPR harmonic and condensate at approximately 417Hz. There are no fewer than four apparently
different RF effects at harmonics of this frequency including ROS, memory
effects, reduced mitotic index and
genotoxic effects. For example, a reduction in GABAA-gated Cl–
channel function during periods of oxidative stress may contribute to the
development of neuronal damage, see Sah et el (2002). It is thus my contention that given a fixed
level of ROS, perturbation of this channel by RF could accentuate its
effects. According to Kishida and Klann
(2007), knowledge of ROS function in the brain also is critical for
understanding aging and neurodegenerative diseases of the brain given that
several of these disorders, including Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson
disease, may be exacerbated by the unregulated generation of ROS. Thus it becomes possible to see how RF via
GABAA-gated Cl– channel function may cause memory effects.
Wondergem
et al (2001) used a non-transformed mouse liver cell line (AML12) was used to
show that blocking swelling-activated membrane Cl− current inhibits
hepatocyte proliferation.
Further,
Cuddapah et al (2013) showed that endogenous
glioma Cl− channels are regulated by TRPC1. Cl− channels could be
an important downstream target of TRPC1 in many other cells types, coupling
elevations in [Ca2+]i to the shape and volume changes associated with migrating
cells. In
chemotaxis assays epidermal growth factor (EGF)-induced invasion was inhibition
by TRPC1 knockdown to the same extent as pharmacological block of Cl−
channels.
Considering
the above, it is proposed that RF at harmonic frequencies of 417 Hz disturbs such
voltage gated chloride channels associated with cellular volume changes and
appropriately blocked can inhibit proliferation, hence the observed changes to
mitotic index.
Lang
et al (2005) show that besides regulating cytosolic Cl− activity,
osmolyte flux and, thus, cell volume, most Cl− channels allow HCO3−
exit and cytosolic acidification, which inhibits cell proliferation and favours
apoptosis.
Examples
of genotoxicity are as follows: loss of
the chloride channel ClC‐7 leads to lysosomal storage disease and
neurodegeneration, see Casper et al (2005).
Mutations of the chloride channels are associated with a wealth of
genetic diseases far too many to reference here.
The
anti-cancer drug cisplatin induces apoptosis by damaging DNA. Pre-treatment of
human adenocarcinoma KB cells with cisplatin for 12 h augmented the magnitude
of VSOR Cl− current. Thus, it is concluded that cisplatin-induced
cytotoxicity in KB cells is associated with augmented activity of a
DIDS-sensitive VSOR Cl− channel and that blockade of this channel is, at
least in part, responsible for cisplatin resistance induced by a stilbene
derivative, see Ise et al (2005). The present author has already filed for
patent protection of and RF method and system in this area.
Oxidative
stress, characterized by overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS), is a
major feature of several pathological states. Indeed, many cancers and
neurodegenerative diseases are accompanied by altered redox balance, which
results from dysregulation of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
(NADPH) oxidase. Avairaimo et al (2010) consider the role of the intracellular
chloride channel 1 (CLIC1) in microglial cells during oxidative stress.
Following microglial activation, CLIC1 translocates from the cytosol to the
plasma membrane where it promotes a chloride conductance. The resultant anionic
current balances the excess charge extruded by the active NADPH oxidase,
supporting the generation of superoxide by the enzyme. In this scenario, CLIC1
could be considered to act as both a second messenger and an executor, see
Avairaimo et al (2010). One can thus
explain the few observations of RF at
417 Hz harmonics as being genotoxic, and we have another mechanism by which RF
can generate ROS.
Once
again at the 417 Hz condensate, every single observation of the effects of RF
radiation can be explained in a consistent manner by the Barnes model.
460 Hz Condensate/Proton
Finally I will discuss the condensate at 460Hz
in coherence with the anhydrous proton ( hydrogen ) IPR harmonic. Initially, it would seem somewhat unclear whether Hv1 channel is
relevant here or not since that fits best with the behaviour of hydrated
protons, hydronium ion in its simplest sense.
As I have shown earlier ions can behave as though they are anhydrous
when squeezed into certain types of Nano pore channel. Sasaki et al (2006) report on ‘A Voltage Sensor-Domain Protein Is a
Voltage-Gated Proton Channel’ I wonder therefore if that is the candidate here
or is one and the same thing as Hv1.
Ramsey
et al (2010) suggest that Hv1 most likely forms an internal water wire for
selective proton transfer and that interactions between water molecules and S4
arginines may underlie coupling between voltage- and pH-gradient sensing. So in this respect I assume that Hv1 is
capable of conduction of protons in any hydration state.
Hv1
is specifically expressed in highly metastatic human breast tumor tissues and
cell lines and Hv1 overexpression is significantly correlated with
clinicopathological parameters and contributes to breast carcinogenesis. High
Hv1 expression is associated with poor progression and unfavourable clinical
outcome of breast cancer, see Wang et al ( 2012). Their results demonstrated
that the inhibition of Hv1 function via knockdown of Hv1 expression can
effectively retard the cancer growth and suppress the cancer metastasis by the
decrease of proton extrusion and the down-regulation of gelatinase activity.
It
can be seen therefore that there is a mechanism for RF to interfere with cell
growth and cell cycle progression on harmonic frequencies of the condensate at
460 Hz. I propose that the exact local
field environment, polarisation and strength will be crucial in determining
which way the protons are driven and hence whether cell growth rate will be
accelerated or diminished.
This
was the final IPR frequency I needed to consider with respect to small
biological ions and once again the Barnes model accounts 100% for all
behaviours seen.
Another test of the Barnes
model: Prediction of increased cancer
rates in geographic regions which have
higher and lower DC magnetic fields than the average 45microtesla.
Changes
in the correspondence of IPR frequencies with Geesink condensates and Schumann
resonance ( SR) modes are summarised in table 4 below:
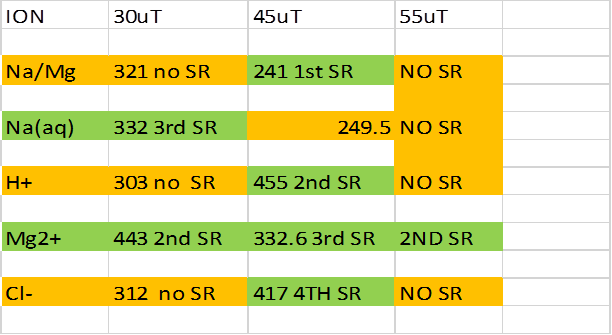
Table 4 : Shows altered
correspondence of IPR resonance with Gessink condensate and presence of absence
of SR mode.
Below,
figure 1 is a map of the world showing geomagnetic field and world cancer incidence.
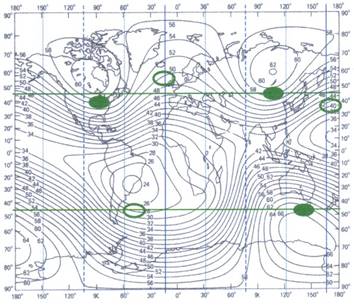
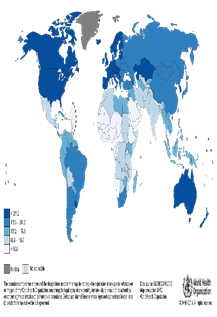
Figure 1
Not
only did I take 45 microtesla as an average field strength but also some
initial IPR data was availed from experiments doe at that field strength. It
is my proposition that human life has evolved from region of the world where in
general the field strength was the order of this value. At such a value most biological processes
involving voltage gated ion channels appear to be protected or governed by
Schumann resonance in some way. I note
that as the field strength drops to 30 microtesla there are only half as many protected processes and at 55
microtesla only 1 protected process.
My guess is cancer rates ought to be proportional to the number of
unprotected processes. Very
approximately this is seen to be the case.
A
4th order polynomial fit, figure 2, of cancer incidence across the
world versus magnetic field strength is particularly instructive. In fact, it suggests that the safest field to live in is 40
microtesla +/- 8.5%. 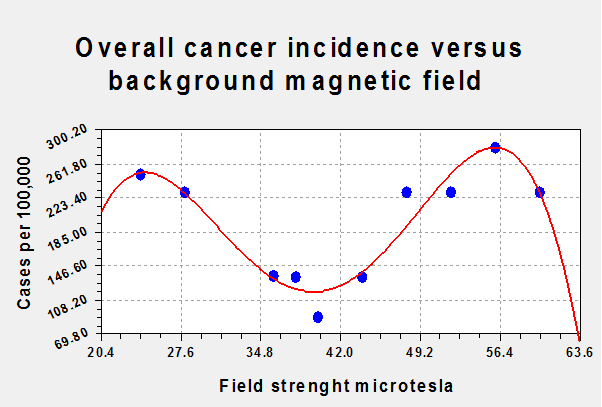
Figure 2: World cancer incidence versus world magnetic
field
This is consistent with
the work of Blackman (1999) using PC12 nerve cells and hydrogen IPR who found
experimentally IPR could be stimulated over abut +-10% bandwidth. The
slight skew in the results is as predicted by the crude estimation above.
Third
test of the Barnes model : Does it
explain Tumour treating Frequencies of Zimmerman et al .
Zimmerman
et al discovered a large number of so
called tumour treating frequencies on the basis of patient biofeedback ( their
heartrate skipped a beat or changed slightly ),said frequencies appear
undisclosed. They also have a patent
specification wherein most frequencies are undisclosed. They have, however,
disclosed .that a small number of frequencies, e.g., 1,873.477 Hz, 2,221.323
Hz, 6,350.333 Hz, and 10,456.383 Hz, were found in the majority of patients
with breast cancer, HCC, prostate cancer, and pancreatic cancer. A further test
of the Barnes model is therefore to reduce the above frequencies onto the
Geesink condensate scale by successive
division by 2 and to see which, if any, voltage gated ion Channels are involved,
see Table 5.
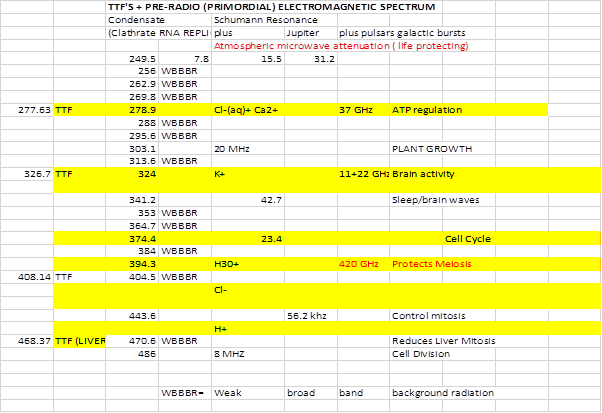
Table 5 : Tumour treating frequencies of Zimmerman et
al reduced to Geesink condensate.
Interestingly
not only will I explain Zimmermann’s frequencies but I will also explain their
‘unusual’ method of bio-feedback selection and further how it helps me narrow
the families of ion channels involved.
Over-expression of various voltage gated channels in cancer cells is
well known. A feature of cancer cells
is that the channels often expressed are those normally found in contractile muscle
or neural tissue and so I propose to look at the common channels in heart muscle
and sensory neurones since firstly, RF perturbation of these is the only way I
see the bio-feedback signal could be generated and secondly when such a signal
is generated I would then expect the same channels in the patient’s cancer
cells to be also modulated. The logic
in looking at sensory neurones in addition to heart muscle is just in case the
effect was generated in sensory neurones adjacent to the heart or neurones elsewhere mapped to the
heart.
Voltage Gated Ion Channels in Heart
and Sensory Neurones
Forward
genetic studies have identified several chloride (Cl-) channel genes, including
CFTR, ClC-2, ClC-3, CLCA, Bestrophin, and Ano1, in the heart. Recent reverse
genetic studies using gene targeting and transgenic techniques to delineate the
functional role of cardiac Cl-. ClC2 is expressed in early postnatal
development in rat brain but shuts down
in adulthood, see Clayton et al ( 1998).
ClC-3 is found in the CNS and Kidney but not really much elsewhere, see Weylandt
et al (2001). Besides the heart, CLCA is
found mainly in glial cells and optic nerve, see Piirsoo et al (2009).
GABA-gated
chloride channels are the main inhibitory neurotransmitter receptors in the
CNS. Conserved domains among members of previously described GABAA receptor
subunits were used to design degenerate sense and antisense oligonucleotides. A
PCR product from this amplification was used to isolate a full-length cDNA. The
predicted protein has many of the features shared by other members of the
ligand-gated ion channel family. This channel subunit has significant amino
acid identity (25–40%) with members of GABAA and GABAC receptor subunits and
thus may represent a new subfamily of the GABA receptor channel. is present in
the electrical conduction system of the human heart. The results of Garret et
al (1997) suggest that novel GABA receptors expressed outside of the CNS may
regulate cardiac function.
Ringer
would be overwhelmed today by the implications of his simple experiment
performed over 120 years ago showing that the heart would not beat in the
absence of Ca2+. Fascination with the role of Ca2+ has proliferated into all
aspects of our understanding of normal cardiac function and the progression of
heart disease, including induction of cardiac hypertrophy, heart failure, and sudden
death. This review examines the role of Ca2+ and the L-type voltage-dependent
Ca2+ channels in cardiac disease. All
three types of calcium channel, L,T and N exist in sensory neurones, see
Nowycky et al ( 1985).
The
sodium cardiac NaV channel is NaV1.5. The human cardiac sodium channel hNaV1.5 is a
member of the family of voltage-gated sodium channels (hNaV1 to 9). The channel
consists of a primary α- and multiple secondary β-subunits. Several NaV channels are involved in
neurones, especially NaV1.7, 1.8 and 1.9.
However, more recently there is also a suggestion that NaV1.5 may act as
a two way mechano transducer and thus be involved as a nervous system touch
receptor, see Morris and Juranka ( 2007).
Heart
muscle also has an inwardly rectifying potassium channel, HERG (formerly ERG1)
and also expressed in the nervous system, see Papa et al (2003). Potassium
leak conductances were recently revealed to exist as independent molecular
entities. The channel is known as
Cardiac
Leak Channel Kcnk3. Kcnk channels are as
fundamental to nerves as they are muscles, see Goldstein et al ( 2001). Kcnk9
( TASK 3) is expressed in nearly all tissues.
In
summery then from above I would expect to search if the same common voltage
gated channels are expressed in tumour
cells and would expect them to be modulated by specific frequencies
accordingly. All tissues also have TRPM7
the ubiquitous non-selective cation channel.
In summary I seek:
1. GABA gated chloride channels.
2. L-type
voltage dependant Ca2+ channels.
3. Sodium
channel Nav1.5.
4. HERG/ERG1.
5. Kcnk3,9 (
TASK 3).
6. TRPM7.
2,221.323 Hz TTF
2,221.323 Hz reduces to 277.63 Hz, very close
to the 278.9 Hz condensate/Ca2+ and Cl-
(aq) IPR coherence. Detail of which has
been discussed extensively above.
Zimmermann et al report that they have no idea of the mechanism of their
treatment but that the mitotic spindle is disrupted. Frequency based
perturbation of both ion channels involved can bring about such effects
see ‘278.9
Hz condensate/Ca2+ and Cl-‘ above.
Further, Anderson et al (1991) has shown the CFTR Cl− channel
contains two predicted nucleotide-binding domains (NBD1 and NBD2). ATP
controls channel activity independent of the R domain and suggested that
hydrolysis of ATP by NBD1 Logically then
if channel activity is also influenced by frequency, ATP levels could be
changed. Channels selective for
potassium or chloride ions are also present in inner mitochondrial membranes.
They probably play an important role in mitochondrial events such as the
formation of delta pH and regulation of mitochondrial volume changes, see Kiciñska
et al (2000). Deecrease in
mitochondria-derived ATP during oxidative stress may cause a disassembly of
mouse MII oocyte spindles, presumably due to the opening of the mitochondrial
PTPs, see Zhang et al 2006. GABA-gated
Cl− channels are expressed in Brain tumours.
Increases
in intracellular free Ca2+ play a major role in many cellular processes. The
deregulation of Ca2+ signaling is a feature of a variety of diseases, and
modulators of Ca2+ signaling are used to treat conditions as diverse as
hypertension to pain. The Ca2+ signal also plays a role in processes important
in cancer, such as proliferation and migration. Many studies in cancer have
identified alterations in the expression of proteins involved in the movement
of Ca2+ across the plasma membrane and subcellular organelles. In some cases,
these Ca2+ channels or pumps are potential therapeutic targets for specific
cancer subtypes or correlate with prognosis, see Monteith
et al (2012).
Wang
et al 2000 conclude that the increase in
mRNA of α1 subunit of the cardiac
isoform of the L-type calcium
channel may be a useful marker of colon cancer compared to other markers
because the increase is large and this increase can be documented on small
samples using a simple semiquantitative reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain
reaction. They found that α1C
protein is increased when colonic cells are nonconfluent or dividing which may
account for the increase in cancer. This
is not only entirely consistent with the Barnes model but also fully vindicates my explanation of
the Zimmerman biofeedback method.
Sato
et al (1994) have stated that calcium channel blockers, phenytoin and verapamil are known to have
fewer side effects than conventional antineoplastic drugs, these results
suggest their possible use in novel therapeutic strategies for pancreatic cancer. Thus the Zimmerman frequencies modulating
calcium channel at 2,221.323 Hz in
addition to chloride is a perfectly feasible way for it to operate and 100%
supported by the Barnes model.
10,454.4 Hz TTF
Reduces
to 326.7 condensate/ potassium channel.
Potassium channels are pore-forming transmembrane proteins that regulate
a multitude of biological processes by controlling potassium flow across cell
membranes. Aberrant potassium channel functions contribute to diseases such as
epilepsy, cardiac arrhythmia, and neuromuscular symptoms collectively known as
channelopathies, see Huang and Jan (2014).
Increasing evidence suggests that
cancer constitutes another category of channelopathies associated with
dysregulated channel expression. Indeed, potassium channel–modulating agents
have demonstrated antitumor efficacy. Potassium channels regulate cancer cell
behaviors such as proliferation and migration through both canonical ion
permeation–dependent and noncanonical ion permeation–independent functions. For
example, Mu et al ( 2003) examined a series of breast cancer samples harboring
amplification of this region and determined that KCNK9 is the sole
overexpressed gene within the amplification epicenter. KCNK9 encodes a
potassium channel that is amplified from 3-fold to 10-fold in 10% of breast
tumors and overexpressed from 5-fold to over 100-fold in 44% of breast tumors.
Overexpression of KCNK9 in cell lines promotes tumor formation and confers
resistance to both hypoxia and serum deprivation, suggesting that its
amplification and overexpression plays a physiologically important role in
human breast cancer. Kim et al (2004)
also state that TASK3 (KCNK9) is found in many cancers and particularly found
overexpression in colorectal cancer. In
this respect the 10,454.4 Hz TTF is
acting as a drug free potassium channel modulator. Such action is perfectly consistent with the
Barnes model.
6530.24 TTF
Reduces
to 408.14 Hz close to but not on either harmonic of hydronium ion or anhydrous
chloride. Within 2% of each so IPR
effects remain feasible.
Hv1
expression is increased in colorectal tumour tissues and cell lines, associated
with poor prognosis, see Wang et al (2013).
The voltage-gated proton channel Hv1 also plays important roles in
proton extrusion and tumour formation by highly metastatic breast cancer cells,
see Hong (2014). Thus RF modulation of Hv1 may be
critical drug free method in controlling
tumour progression and again entirely consistent with the Barnes model.
Peretti et al (2014) have
recently disclosed chloride intracellular ionic channels (CLICs) are involved
in cancer development. For instance:
•CLIC1 and CLIC4 in particular are overexpressed in
cancer stem cells.
•Both proteins are largely present in the cytoplasm
of tumorigenic cells.
•In cancer stem cells, they have a functional
expression as membrane ionic channels.
•This peculiar localization may offer a unique
target for cancer therapy.
More recently, CLC, CLIC, and CLCA intracellular
chloride channels have been recognized for their contributions in modifying
cell cycle, apoptosis, cell adhesion, and cell motility.
Thus RF modulation of these channels may yield a critical and
highly tuneable drug free method in controlling tumour progression and again
entirely consistent with the Barnes model and in all probability may be the
very channels being stimulated by Zimmerman.
The final
test of the model can it explain locations which have high cancer incidence on
basis of RF spectrum?
IPR can be activated over a range of frequencies
about +/-10% , thus I have included this in Table 6 below. This also lines up with a number of
biological effects on apparently different condensates but yet which associate
specifically with a certain kind of ion channel.
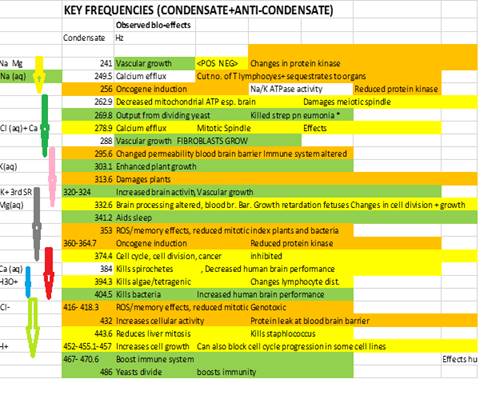
Table 6 : Yellow arrow = sodium = 241-256 Hz , Dark green arrow = aqueous chloride, dry
calcium ( nanopore effect) =262-295 Hz,
Pink arrow Potassium =
295-332 Hz, Grey arrow= Magnesium
specifically TRPM7 Channel 320-374 Hz,
Red arrow = Hydrated calcium 374-404 Hz,
Blue arrow HV1 Proton channel centre 394 Hz, pale green arrow = Anhydrous chloride (
nanopore) 416-457 Hz.
All
the observed biological effects within each frequency band can be accounted for
by specific ion channels and the assumption is that each nearby mode of the condensate is capable of
providing membrane vibrational energy. In addition to the predicted power banding
effects it is feasible that phase effects on each nearby mode modulate the IPR
kinetics as to provide channel enhancement or blocking effect.
Considering
all the possible condensate frequencies, I hypothesise that the range
corresponding to voltage gated chloride could be most dangerous . To
re-iterate, Avairaimo et al (2010)
consider the role of the intracellular chloride channel 1 (CLIC1) in microglial
cells during oxidative stress. Following microglial activation, CLIC1
translocates from the cytosol to the plasma membrane where it promotes a
chloride conductance. The resultant anionic current balances the excess charge
extruded by the active NADPH oxidase, supporting the generation of superoxide
by the enzyme. In this scenario, CLIC1 could be considered to act as both a
second messenger and an executor, see Avairaimo et al (2010). One can thus explain the few observations of RF at 416-457 Hz harmonics as being
genotoxic, and we have another mechanism by which RF can generate ROS.
Further
TRPM7 is highly expressed in a number of human cancer tissues and cell lines.
Mg2+ has an essential role in TRPM7's control of cell survival and in the
regulation of cellular ROS levels, see Chen et al 2012. I
wonder if RF exposure on these frequencies may be benficial?
It
is most instructive to consider the frequency spectrum at a location where a
triple negative breast cancer victim and young stroke victim both live. See table 7 below:
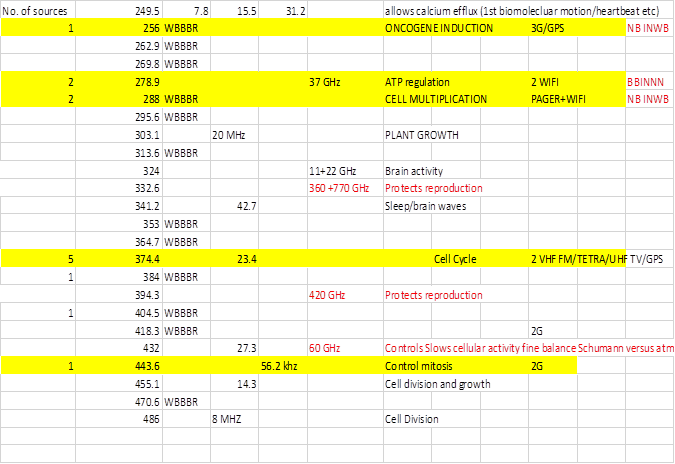
Table 7 : Frequency spectrum at house of an
aggressive triple negative breast cancer case.
Notice
there are 5 separate frequency sources with harmonics that could cause modulation of the TRPM7
channel and a further two 2G
mobile phone frequencies affecting the intracellular
chloride channel 1. I will call this I/C
ratio 2/5. I = ROS INITIATION C= ROS
CONTROL DISRUPTION.
In
another location with animal cancer
(dog) the ratio was 2/3. In a
nearby location with cat and human colorectal cancer the ratio was also 2/3.
In
a location with no cancer the I/C ratio was 3/2.
I propose that in the initiation
phase RF produces ROS ( SUPEROXIDE) but
that in normal circumstances the body could regulate this but that when TRPM7 is modulated by excessive frequency sources both additional oxidative and nitrosative
stresses occur and either initiation of cancer or promotion of existing cancer follow. This could account for why certain cancer
latency or reoccurrence periods appear to be reducing. Certainly ionising radiation has this effect
for breast cancer, see Nguyen et al (2011).
There
is enormous support for the Barnes model in the existing literature in teat
numerous anti-oxidants including for example, but not limited to ; melatonin (ref) , caffeic acid phenethyl
ester (ref) , vitamins E and C (ref) , garlic extract (ref) , Ginkgo biloba (ref) and Zinc (ref) are reported to produce protection from or improve the severity of RF radiation
damage in tissue or cell culture.
Power Effects
In
the Barnes quantum mechanical model pertinent to the influence of frequency on
biological systems, when that ‘frequency’ is provided by an electromagnetic
wave I also predict power effects
directly via the AC magnetic field component of the wave.
It
is possible to predict the order of magnitude of the power effects as
follows. The earth’s static B field is
of the order of 50 microtesla. Schumann resonance field strengths are of the
order a few picotesla. I have
suggested how important the synchronisation of Schumann resonance with certain
key ion IPR frequencies and coherent condensate frequencies in biology handed
down from its primordial origins. Persinger
(2014) too has emphasised the importance of this for the human brain. While Persinger (2015) finds direct evidence
of Schuman resonance coherence with measured Spectral Power Densities (SPD)
within the Quantitative Electroencephalographic (QEEGs). Profiles of 41 men and women displayed
repeated transient coherence with the first three modes (7 - 8 Hz, 13 - 14 Hz,
and 19 - 20 Hz) of the Schumann Resonance in real time. The duration of the
coherence was about 300 ms about twice per min. Topographical map clusters
indicated that the domain of maximum coherence was within the right caudal
hemisphere near the Parahippocampal gyrus. These clusters, associated with
shifts of about 2 μV, became stable about 35 to 45 ms after the onset of
the synchronizing event. During the first 10 to 20 ms, the isoelectric lines
shifted from clockwise to counter-clockwise rotation. The results are
consistent with the congruence of the frequency, magnetic field intensity,
voltage gradient, and phase shifts that are shared by the human brain and the
earth ionospheric spherical wave guide, and is also
in agreement with my theories of sleep ( refs).
Indeed
Persinger’s work provides incredible support for the general logic of the Barnes model.
The
average RF field strength in a number of premises I have visited with cancer
cases was .11v/m, see http://www.drchrisbarnes.co.uk/CancerHouses.htm. In houses without cancer the average field
strength was .019 V/m. The equivalent
magnetic field strengths are 370 and 63 picotesla respectively. Taking the dozen or so strongest frequencies on the power spectrum which in
this area often include 2G (900 MHz), 3G (2100 MHz), wifi, TETRA (390 MHz), UHF
TV 670 MHZ, VHF pagers 153 MHz and vhf
FM (90-100 MHZ) as contributing this
yields an average of some 30 picotesla per frequency in cancer houses about 5 picotesla per frequency at the
locations without cancer. Assuming each
Schumaan resonance provides about 1 pictotesla and the first 5 are active in the
human body, this also yields about 5
picotesla.
Thus
it would seem, possibly this is about the threshold that needs overwhelming to
produce biological effect. In line with
quantum processes it is interesting to see that the field strengths associated
with cancer are whole number multiples, in this case 6 times this specified magnetic field strength. Looking at other known instances of
bio-sensitivity, the field some 20 cm away from an average WIFI laptop is of
the order of .22 V/m, or 125 picotesla.
This is an integer multiple of the above calculated ‘bio-active’ field
above and several sensitive individuals including the present author have
notice skin tingling and eye burning when using laptops at this range.
RF Polarisation and cancer.
Very
recently indeed it has been disclosed that countries which have horizontally
polarised FM radio have more cases of melanoma. In 2002, a Hallberg and Johannsen made a detailed analysis of skin melanoma in 289
Swedish municipalities showed a strong association with the number of
horizontally polarized main FM transmitters covering a municipality. Basic
antenna theory says that body-resonance and standing waves cannot appear above
a metal spring mattress unless the electric field is horizontally polarized. To
test the hypothesis that body-resonant radiation can cause increased cancer
risk in other European countries, I collected and analysed reported data from
24 countries, among which six were using vertical polarization. The results
showed a strong association between cancer risk and the use of horizontally
polarized FM broadcasting radiation, whereas vertical polarization seemed to
cause no health effects. This information should form the basis for initiating
relevant corrective actions by responsible authorities. This elegantly fits the IPR hypothesis since
IPR is modulated by an AC ( magnetic) field when it is parallel to the earth’s DC field, (ref), and in an horizontal EM wave
the E FIELD IS HORIZONTAL AND THE H-FIELD VERTICAL ( i.e. parallel to the earth
field).
Pulsed healing fields
Traditionally,
pulsed electric and magnetic fields have been used for a variety of tissue
healing scenarios. Getting them working
has been almost a black art, where mostly ad hoc techniques have bene
employed. If the pulses are of
sufficient magnitude and short duration enough , electroporation occurs.
However, in the majority of cases this may not be the case. A pulse simply contains a broad spectrum of
frequency and therefore activates wanted and unwanted cellular processes
simultaneously. The Barnes hypothesis
will allow proper tuning of wound healing systems.
Conclusions
A
new hypothesis has been formulated which brings together Bose Einstein (
Frolich ) condensate ‘Geesink’ modes and
Ion Parametric Resonance. Key frequencies work in concert with Schumann
resonance to normalise biological systems at an ideal DC field strength. The hypothesis enjoys strong support in a
number of directions. For example, the prediction that cancer incidences would
vary according to the earth’s background DC field is fulfilled. A number of healing frequencies are
fully explained in terms of the particular ion channel being disturbed
especially pertinent to cancer wherein cancer cells some ion channels are
overexpressed. Perturbation of very specific ion channels
also explains dangerous effects of RF on biology. Activation of voltage gated chloride
channels is most dangerous and
explains the few observations
of RF at harmonics of 455-457 Hz as being genotoxic and
a mechanism by which RF can generate
ROS. Under normal circumstances THE BODY CAN
COPE WITH THIS but I propose that if voltage gated channel TRPM7 is also modulated by excessive
frequency sources at harmonics of 320-374 Hz
both additional oxidative and nitrosative stresses occur and either initiation
of cancer could follow or highly
likely promotion of existing cancer will
follow. This could account for why
certain cancer latency or reoccurrence periods appear to be reducing. Certainly ionising radiation has this effect
for breast cancer, see Nguyen et al
(2011). Another great success of the
theory is to explain why the team of Zimmerman and Pasche were able to use
physiological heartbeat changes to define their so called ‘TTF’ tumour treating
frequencies. The same sorts of ion
channels expressed in heart muscle and nerve fibres are also expressed in many
cancer cells but not so much normal non-excitable tissue. The theory also explains Hallberg’s observations of FM radio and melanoma. Finally, regarding power windowing, the limit
of human sensitivity is of the order of 1picotesla, i.e. pretty much the same
as Schumann resonance.
Acknowledgments
The
author acknowledges his wife Gwyneth, his son Dwain and Mr Mike Jenkins for
stimulating and interesting discussions on the topic.
References
An
extensive reference list will be published in due course.